Clinical Evidence – Select the category you want to view
Title
Efficacy of Monitoring Devices in Support of Prevention of Pressure Injuries
Key Takeaway/s
This Johns Hopkins-led meta-analysis reports that the use of pressure monitoring is associated with an 88% reduction in the risk of developing pressure injuries, demonstrating their effectiveness as a clinical prevention tool. Read Full Article
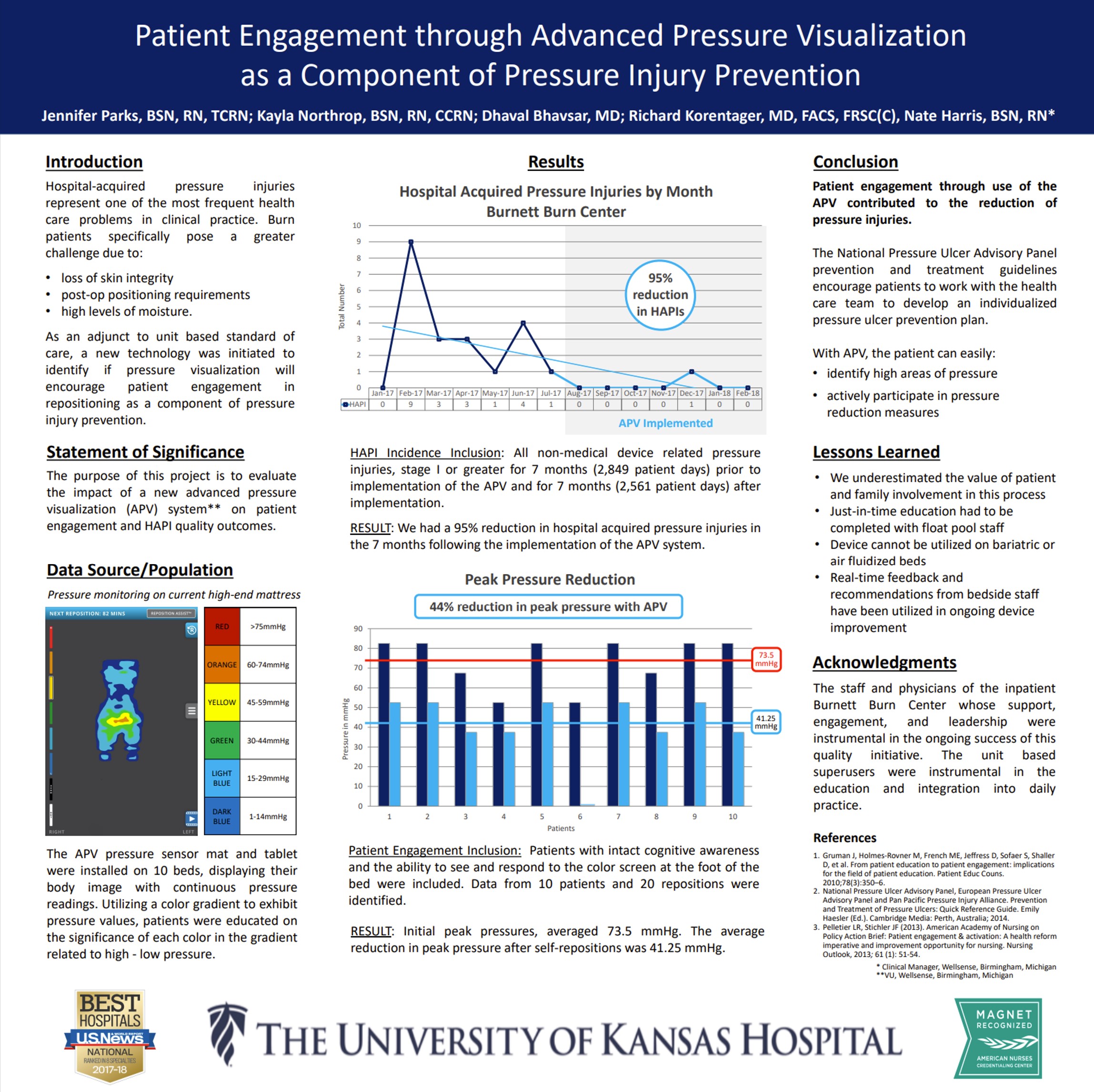
Title
Key Takeaway/s
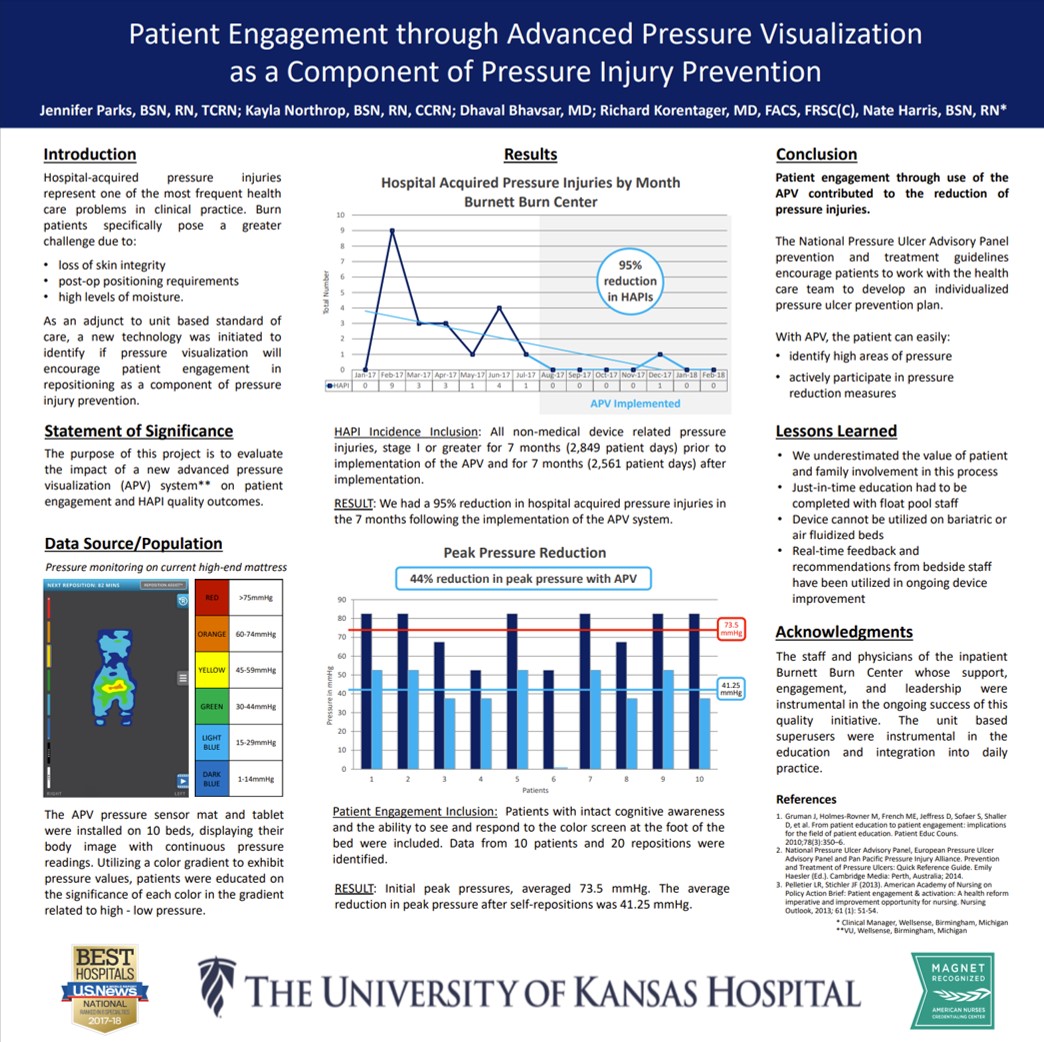
At the University of Kansas Hospital Burnett Burn Center, Advanced Pressure Visualization resulted in a 95% reduction in hospital-acquired pressure injuries (27 down to 1) and a 44% reduction in peak pressures, showing the effectiveness of patient engagement with real-time pressure feedback. Read Full Article
Title
Patient repositioning and pressure ulcer risk – Monitoring interface pressures of at-risk patients
Key Takeaway/s
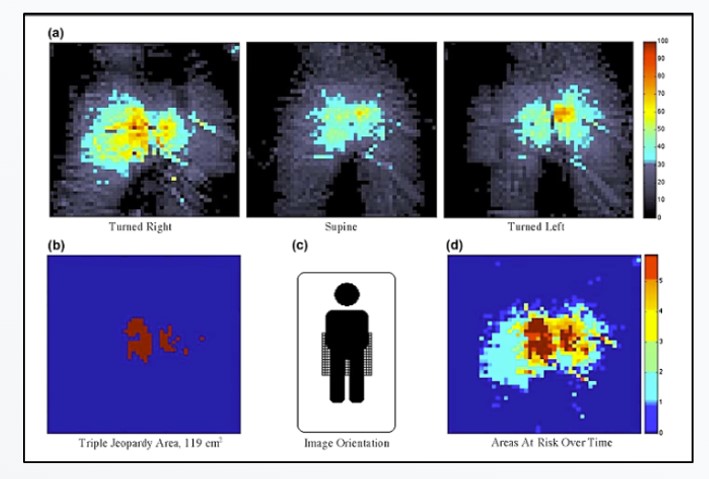
This peer-reviewed University of Florida study found that after repositioning, elevated sacral pressure persisted in over 95% of turns, leaving patients at ongoing pressure injury risk. The findings show that turning alone does not reliably offload pressure and that pressure visualization is needed to confirm effective offloading. Read Full Article
Title
Dynamic Physiologic Skin Monitoring to Enhance a Pressure Ulcer Prevention Program
Key Takeaway/s
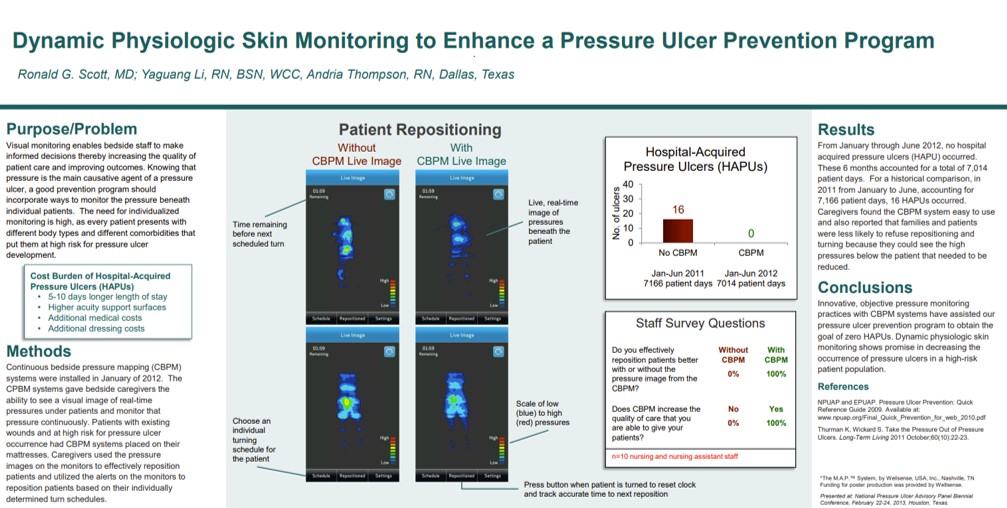
Methodist Dallas Medical Center achieved 100% elimination of hospital-acquired pressure ulcers over 7,014 patient days with continuous pressure visualization, compared to 16 HAPUs the prior year with visualization. Staff reported 100% agreement that visualization improved repositioning effectiveness and reduced pressure exposure. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In a retrospective analysis at Henry Ford Hospital’s medical ICU, continuous bedside pressure mapping reduced pressure ulcer incidence by 94% and was reported by staff to improve repositioning effectiveness, comfort, and adherence to protocols. Read Full Article
Title
Real-Time Pressure Assessment and Monitoring Improves Patient Care
Key Takeaway/s
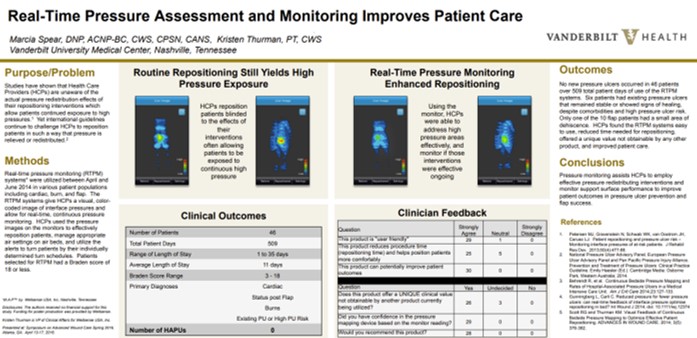
At Vanderbilt University Medical Center, real-time pressure visualization was used in 46 patients across 509 patient-days, resulting in zero new pressure injuries, high clinician satisfaction, improved repositioning effectiveness and patient comfort. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
At the Johns Hopkins Burn Center, real-time pressure mapping reduced the hospital-acquired pressure injury rate by 44.4%, eliminated full-thickness pressure injuries, and lowered costs by 43.8%, demonstrating significant effectiveness in the burn ICU. Read Full Article
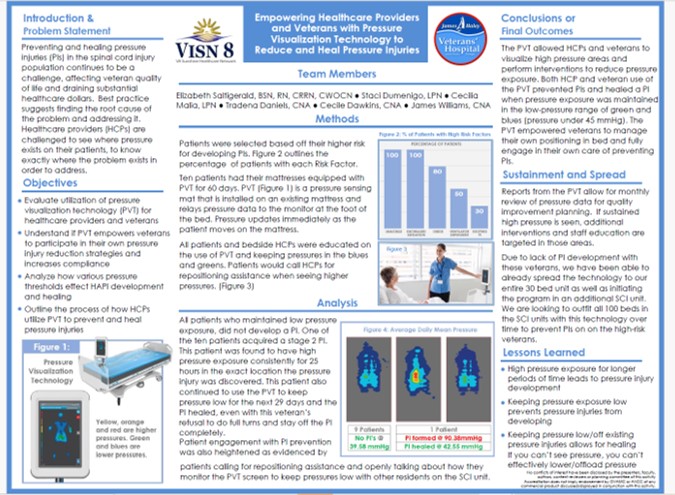
Title
Key Takeaway/s
A clinical poster from the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital (VISN 8) showed that with pressure visualization technology, 90% of high-risk spinal cord injury patients avoided new pressure injuries, and existing Stage 2 injuries healed when pressure was reduced. Read Full Article
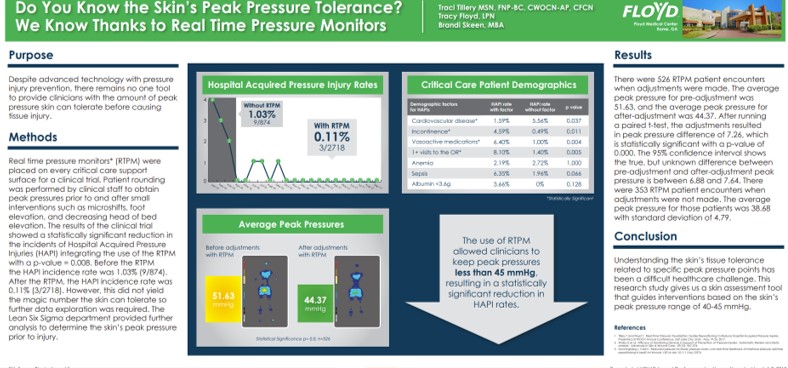
Title
Do You Know the Skin’s Peak Pressure Tolerance? We Know Thanks to Real Time Pressure Monitors
Key Takeaway/s
This Floyd Medical Center poster showed that using real-time pressure monitoring reduced hospital-acquired pressure injuries (HAPIs) by nearly 90% and enabled staff to maintain peak pressures below ~45 mmHg, a threshold associated with significantly lower HAPI rates. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Overall, the annual prevalence of pressure injuries and annual mean hospitalization cost increased ($69,499.29 to $102,939.14). Read Full Article
Title
Value of hospital resources for effective pressure injury prevention: a cost-effective analysis
Key Takeaway/s
This peer-reviewed BMJ Quality & Safety cost-effectiveness study analyzed 34,000+ hospital patients and quantified the financial impact of severe pressure injuries. It reported that Stage 3–4 (full-thickness) pressure injuries add about $6,209 per patient-day, underscoring the high daily cost burden and the value of effective, hospital-wide prevention. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
HAPIs materially increase hospital resource use, with an average incremental cost of $21,767 per HAPI and higher total costs with increasing stage severity. Read Full Article
Title
The national cost of hospital-acquired pressure injuries in the United States
Key Takeaway/s
This analysis estimates the average incremental hospital cost is ~$10,708 per HAPI across all stages. Costs are concentrated in severe ulcers: Stage 3 and 4 injuries represent a small fraction of cases but account for about 59% of total HAPI costs, meaning severe, full-thickness ulcers consume the majority of spending. Read Full Article
Title
High cost of stage IV pressure ulcers
Key Takeaway/s
This study from NYU School of Medicine found Stage IV pressure ulcers cost about $125k–$129k per patient in hospital treatment costs when ulcer-related complications were included. These costs are far higher than prior estimates and emphasize early recognition and treatment to stop progression to Stage IV and avoid extreme, non-reimbursed “never event” costs. Read Full Article
Title
Cost of Treating Pressure Ulcers for Veterans with Spinal Cord Injury
Key Takeaway/s
“In a VA study of veterans with spinal cord injury, the presence of a pressure injury increased average health care costs by $77,587 compared to those without, driven by higher inpatient costs, emphasizing the need for prevention.” Read Full Article
Title
Pressure Ulcers: Impact on Hospital Costs and Length of Stay
Key Takeaway/s
This University of Alabama at Birmingham hospital study found that developing a hospital-acquired Stage II+ pressure ulcer was associated with substantially higher hospital costs and longer stays. Mean unadjusted costs were $37,288 vs $13,924 and LOS 30.4 vs 12.8 days. Even after adjustment, costs and LOS remained significantly higher. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
This UAB tertiary teaching-hospital study found that patients who developed hospital-acquired pressure ulcers incurred substantially higher costs and longer stays. Adjusted analyses showed costs of $29,048 vs $13,819 and length of stay of 20.9 vs 12.7 days, confirming pressure ulcers independently drive excess inpatient utilization beyond baseline severity. Read Full Article
Title
Hospitalizations Related to Pressure Ulcers among Adults 18 Years and Older, 2006
Key Takeaway/s
AHRQ HCUP data show pressure-ulcer–related adult hospitalizations carried materially higher utilization and cost: mean stay 12.7–14.1 days vs 5.0 days without pressure ulcers, and mean cost per stay $16,800–$20,400 vs $9,900. Over half were discharged to long-term care, and mortality was higher. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In elderly care, pressure mapping directly supported staff education by improving pressure-injury awareness, strengthening repositioning decisions with visual feedback, and increasing the frequency and appropriateness of preventative interventions during routine care. Read Full Article
Title
Pressure Map Technology for Pressure Ulcer Patients: Can We Handle the Truth?
Key Takeaway/s
Pressure mapping improved workflow performance in a long-term acute care setting by reducing delays to scheduled turning, supporting more reliable execution of turning protocols, and creating clearer accountability around when repositioning actually occurs. Read Full Article
Title
Self-turning for Pressure Injury Prevention
Key Takeaway/s
Pressure visualization can be used as a structured education tool for appropriate patients, enabling them to learn and reliably perform self-repositioning with clear visual guidance, reducing staff burden while keeping turning technique verifiable. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Across multiple care settings, the evidence supports pressure visualization as a workforce enablement tool: it makes prevention practices more consistent, improves staff decision-making with real-time feedback, and strengthens training and standardization of repositioning technique. Read Full Article
Title
Self-turning for Pressure Injury Prevention
Key Takeaway/s
When appropriate patients were identified as able to self-turn, real-time pressure visualization helped them reposition themselves reliably with clear, immediate feedback. This demonstrates that pressure visualization can actively engage patients in their own pressure management, supporting safer self-directed turning when clinically appropriate. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
This study frames pressure visualization as a patient-facing tool: by making pressure visible, it motivates participation and supports behavior change around repositioning. The work reinforces that engagement improves when patients can see the cause-and-effect of their own movement on pressure. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In a veteran population, pressure visualization was used not only to guide clinical care but to empower patients and caregivers with understandable, visual information about pressure risk. This supports greater patient involvement in day-to-day positioning decisions and reinforces shared accountability for prevention and healing. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In two acute orthopedic trauma wards, patients and families reported the pressure visualization system was helpful, indicating strong engagement with the care process. The findings suggest that making pressure visible can improve patient and family understanding of repositioning goals and increase participation in prevention efforts. Read Full Article