Clinical Evidence – Select the category you want to view
Title
Pressure Map Technology for Pressure Ulcer Patients: Can We Handle the Truth?
Key Takeaway/s
In a 55-bed LTAC facility in North Texas, pressure mapping technology improved nursing practice, reducing average turn delays by 63% and median delays by 56%, thereby lowering risk of tissue damage. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
With the use of real-time pressure mapping feedback, student nurses were able to significantly reduce interface pressure compared to repositioning without the system, demonstrating its value in teaching effective pressure ulcer prevention. Read Full Article
Title
Pressure Mapping: A New Path to Pressure-Ulcer Prevention
Key Takeaway/s
This clinical article from American Nurse explains that pressure mapping provides visual, real-time information on pressure distribution, allowing clinicians to see high-pressure areas and verify whether repositioning and support surface interventions are actually relieving pressure, rather than relying solely on skin assessment or patient feedback. Read Full Article
Title
The wound/burn guidelines – 2: Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment for pressure ulcers
Key Takeaway/s
These Japanese Dermatological Association guidelines state that pressure injury prevention depends on confirming actual interface pressure. They direct caregivers to check sacral pressure with an interface pressure meter, reinforcing that effective repositioning must be guided by measured pressure rather than routine practice. Read Full Article
Title
Understanding and Treating Suspected Deep Tissue Injury
Key Takeaway/s
A Henry Ford Hospital elderly patient presented with a deep tissue injury (DTI), which was fully resolved within 11 days using real-time pressure monitoring, with no additional ulcers developing. Read Full Article
Title
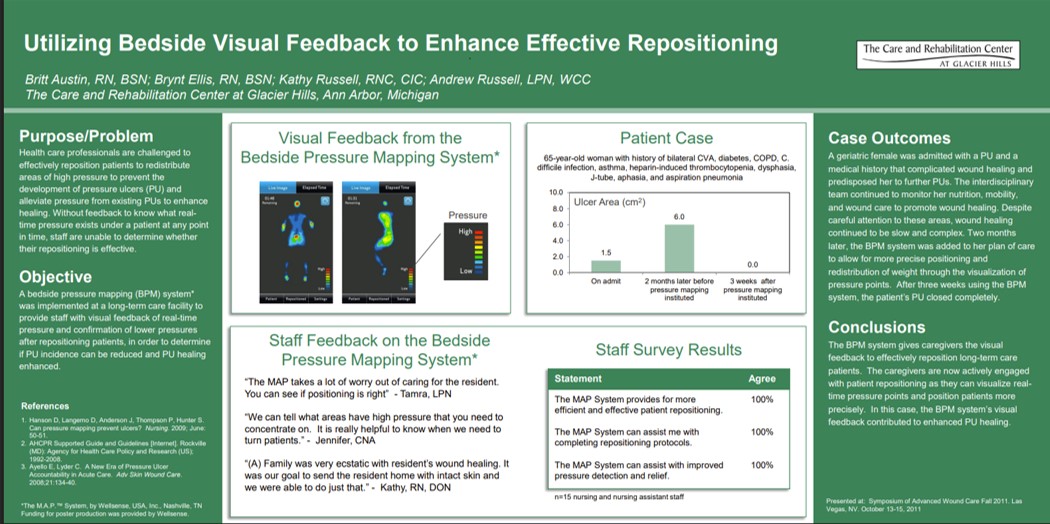
Utilizing Bedside Visual Feedback to Enhance Effective Repositioning
Key Takeaway/s
A 65-year-old long-term care patient at Glacier Hills with a non-healing pressure ulcer achieved complete wound closure within 3 weeks after the introduction of real-time bedside pressure visualization to guide repositioning. Read Full Article
Title
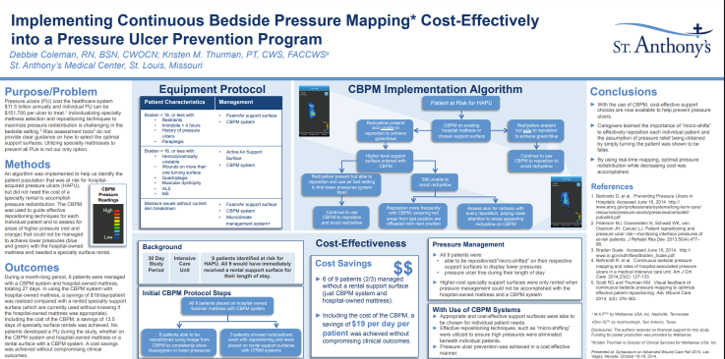
Pressure Mapping with Visual Feedback to Enhance a Pressure Ulcer Prevention Program
Key Takeaway/s
Henry Ford Health System utilized real-time pressure mapping with visual feedback to enhance pressure ulcer prevention, confirming effective repositioning for patients and gaining acceptance from caregivers and patients. The technology showed immediate benefits in identifying and adjusting patient positions to prevent ulcer development. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Increasing HAPI stage is associated with higher in-hospital mortality, higher risk of other HACs, and 1.5 to 2x higher 30, 60, and 90-day readmissions. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
This Hopkins burn ICU study found that implementing real-time pressure mapping reduced HAPI-related care costs from about $6,750 to $3,800 per patient. These savings reflect direct pressure-injury treatment costs only (e.g., wound care), not systemic complications or extended hospitalization, and were driven by fewer and less severe pressure injuries Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
At St. Anthony’s Medical Center, Continuous Bedside Pressure Mapping enabled use of lower-cost support surfaces, reducing reliance on specialty rentals and delivering net savings of $19 per patient per day after including the cost of the visualization system itself. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In elderly care, pressure mapping directly supported staff education by improving pressure-injury awareness, strengthening repositioning decisions with visual feedback, and increasing the frequency and appropriateness of preventative interventions during routine care. Read Full Article
Title
Pressure Map Technology for Pressure Ulcer Patients: Can We Handle the Truth?
Key Takeaway/s
Pressure mapping improved workflow performance in a long-term acute care setting by reducing delays to scheduled turning, supporting more reliable execution of turning protocols, and creating clearer accountability around when repositioning actually occurs. Read Full Article
Title
Self-turning for Pressure Injury Prevention
Key Takeaway/s
Pressure visualization can be used as a structured education tool for appropriate patients, enabling them to learn and reliably perform self-repositioning with clear visual guidance, reducing staff burden while keeping turning technique verifiable. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Across multiple care settings, the evidence supports pressure visualization as a workforce enablement tool: it makes prevention practices more consistent, improves staff decision-making with real-time feedback, and strengthens training and standardization of repositioning technique. Read Full Article
Title
Self-turning for Pressure Injury Prevention
Key Takeaway/s
When appropriate patients were identified as able to self-turn, real-time pressure visualization helped them reposition themselves reliably with clear, immediate feedback. This demonstrates that pressure visualization can actively engage patients in their own pressure management, supporting safer self-directed turning when clinically appropriate. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
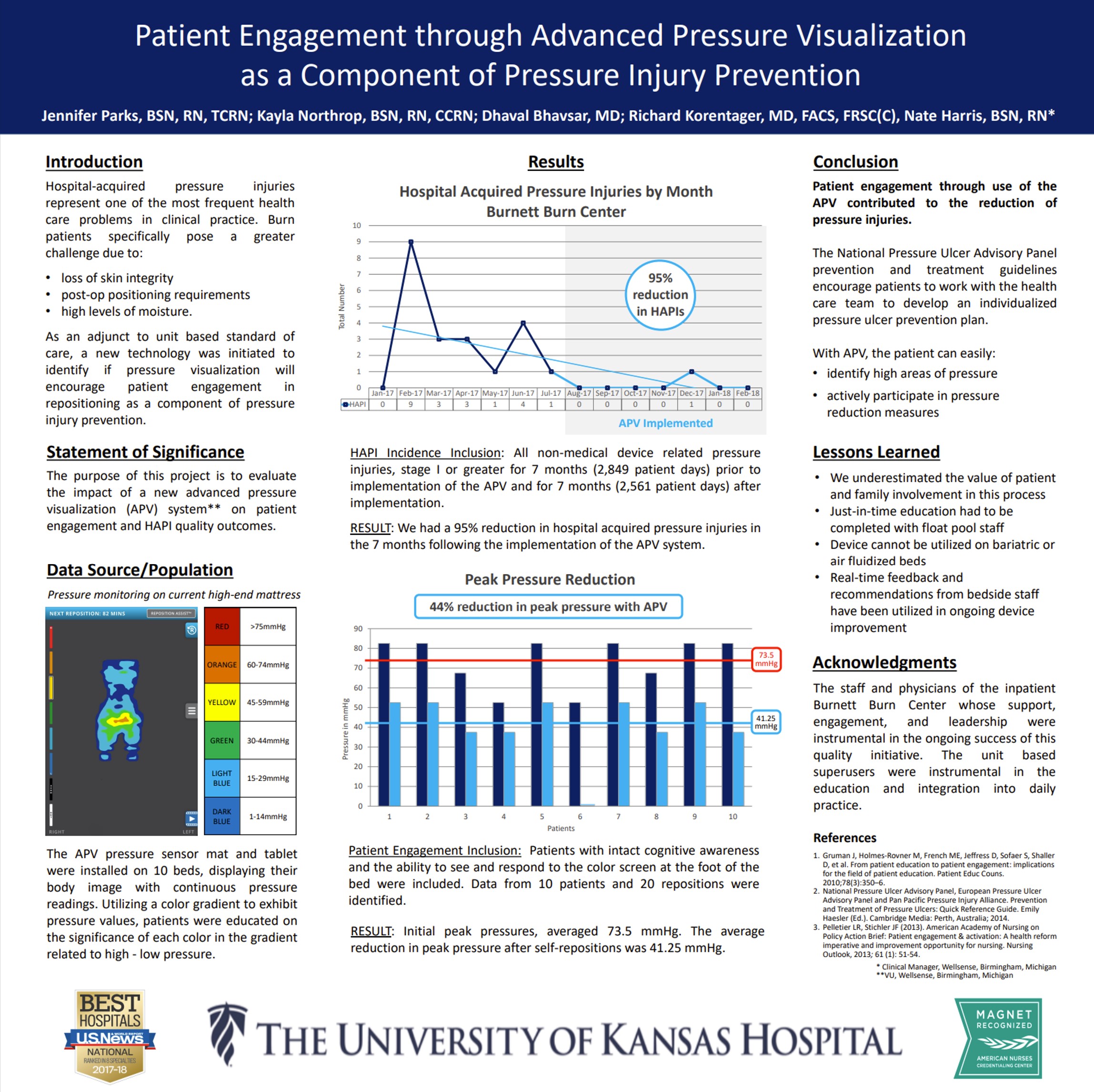
This study frames pressure visualization as a patient-facing tool: by making pressure visible, it motivates participation and supports behavior change around repositioning. The work reinforces that engagement improves when patients can see the cause-and-effect of their own movement on pressure. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
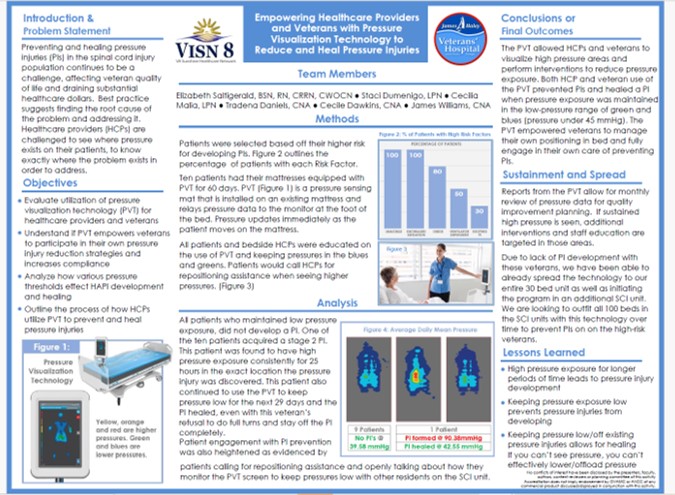
In a veteran population, pressure visualization was used not only to guide clinical care but to empower patients and caregivers with understandable, visual information about pressure risk. This supports greater patient involvement in day-to-day positioning decisions and reinforces shared accountability for prevention and healing. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In two acute orthopedic trauma wards, patients and families reported the pressure visualization system was helpful, indicating strong engagement with the care process. The findings suggest that making pressure visible can improve patient and family understanding of repositioning goals and increase participation in prevention efforts. Read Full Article