Clinical Evidence – Select the category you want to view
Title
Pressure Map Technology for Pressure Ulcer Patients: Can We Handle the Truth?
Key Takeaway/s
In a 55-bed LTAC facility in North Texas, pressure mapping technology improved nursing practice, reducing average turn delays by 63% and median delays by 56%, thereby lowering risk of tissue damage. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
With the use of real-time pressure mapping feedback, student nurses were able to significantly reduce interface pressure compared to repositioning without the system, demonstrating its value in teaching effective pressure ulcer prevention. Read Full Article
Title
Pressure Mapping: A New Path to Pressure-Ulcer Prevention
Key Takeaway/s
This clinical article from American Nurse explains that pressure mapping provides visual, real-time information on pressure distribution, allowing clinicians to see high-pressure areas and verify whether repositioning and support surface interventions are actually relieving pressure, rather than relying solely on skin assessment or patient feedback. Read Full Article
Title
The wound/burn guidelines – 2: Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment for pressure ulcers
Key Takeaway/s
These Japanese Dermatological Association guidelines state that pressure injury prevention depends on confirming actual interface pressure. They direct caregivers to check sacral pressure with an interface pressure meter, reinforcing that effective repositioning must be guided by measured pressure rather than routine practice. Read Full Article
Title
Understanding and Treating Suspected Deep Tissue Injury
Key Takeaway/s
A Henry Ford Hospital elderly patient presented with a deep tissue injury (DTI), which was fully resolved within 11 days using real-time pressure monitoring, with no additional ulcers developing. Read Full Article
Title
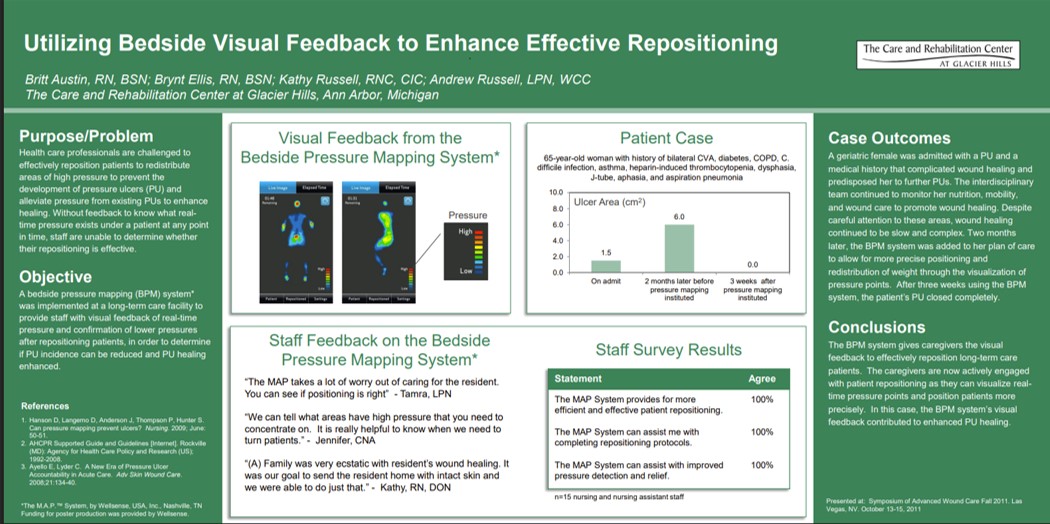
Utilizing Bedside Visual Feedback to Enhance Effective Repositioning
Key Takeaway/s
A 65-year-old long-term care patient at Glacier Hills with a non-healing pressure ulcer achieved complete wound closure within 3 weeks after the introduction of real-time bedside pressure visualization to guide repositioning. Read Full Article
Title
Pressure Mapping with Visual Feedback to Enhance a Pressure Ulcer Prevention Program
Key Takeaway/s
Henry Ford Health System utilized real-time pressure mapping with visual feedback to enhance pressure ulcer prevention, confirming effective repositioning for patients and gaining acceptance from caregivers and patients. The technology showed immediate benefits in identifying and adjusting patient positions to prevent ulcer development. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Increasing HAPI stage is associated with higher in-hospital mortality, higher risk of other HACs, and 1.5 to 2x higher 30, 60, and 90-day readmissions. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Overall, the annual prevalence of pressure injuries and annual mean hospitalization cost increased ($69,499.29 to $102,939.14). Read Full Article
Title
Value of hospital resources for effective pressure injury prevention: a cost-effective analysis
Key Takeaway/s
This peer-reviewed BMJ Quality & Safety cost-effectiveness study analyzed 34,000+ hospital patients and quantified the financial impact of severe pressure injuries. It reported that Stage 3–4 (full-thickness) pressure injuries add about $6,209 per patient-day, underscoring the high daily cost burden and the value of effective, hospital-wide prevention. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
HAPIs materially increase hospital resource use, with an average incremental cost of $21,767 per HAPI and higher total costs with increasing stage severity. Read Full Article
Title
The national cost of hospital-acquired pressure injuries in the United States
Key Takeaway/s
This analysis estimates the average incremental hospital cost is ~$10,708 per HAPI across all stages. Costs are concentrated in severe ulcers: Stage 3 and 4 injuries represent a small fraction of cases but account for about 59% of total HAPI costs, meaning severe, full-thickness ulcers consume the majority of spending. Read Full Article
Title
High cost of stage IV pressure ulcers
Key Takeaway/s
This study from NYU School of Medicine found Stage IV pressure ulcers cost about $125k–$129k per patient in hospital treatment costs when ulcer-related complications were included. These costs are far higher than prior estimates and emphasize early recognition and treatment to stop progression to Stage IV and avoid extreme, non-reimbursed “never event” costs. Read Full Article
Title
Cost of Treating Pressure Ulcers for Veterans with Spinal Cord Injury
Key Takeaway/s
“In a VA study of veterans with spinal cord injury, the presence of a pressure injury increased average health care costs by $77,587 compared to those without, driven by higher inpatient costs, emphasizing the need for prevention.” Read Full Article
Title
Pressure Ulcers: Impact on Hospital Costs and Length of Stay
Key Takeaway/s
This University of Alabama at Birmingham hospital study found that developing a hospital-acquired Stage II+ pressure ulcer was associated with substantially higher hospital costs and longer stays. Mean unadjusted costs were $37,288 vs $13,924 and LOS 30.4 vs 12.8 days. Even after adjustment, costs and LOS remained significantly higher. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
This UAB tertiary teaching-hospital study found that patients who developed hospital-acquired pressure ulcers incurred substantially higher costs and longer stays. Adjusted analyses showed costs of $29,048 vs $13,819 and length of stay of 20.9 vs 12.7 days, confirming pressure ulcers independently drive excess inpatient utilization beyond baseline severity. Read Full Article
Title
Hospitalizations Related to Pressure Ulcers among Adults 18 Years and Older, 2006
Key Takeaway/s
AHRQ HCUP data show pressure-ulcer–related adult hospitalizations carried materially higher utilization and cost: mean stay 12.7–14.1 days vs 5.0 days without pressure ulcers, and mean cost per stay $16,800–$20,400 vs $9,900. Over half were discharged to long-term care, and mortality was higher. Read Full Article
Title
Pressure Mapping: A New Path to Pressure-Ulcer Prevention
Key Takeaway/s
Pressure mapping gives clinicians immediate visual feedback on where pressure remains, turning “best-practice” repositioning into a teachable, repeatable workflow. It helps staff validate that a turn or support-surface change actually relieved pressure, rather than relying on skin checks, habit, or patient report. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Real-time pressure feedback accelerates skills training by showing student nurses, instantly, whether a positioning change actually reduces interface pressure. This turns pressure-injury prevention from a theoretical lesson into a measurable competency and supports more consistent technique across learners and instructors. Read Full Article
Title
The wound/burn guidelines – 2: Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment for pressure ulcers
Key Takeaway/s
These guidelines reinforce a workflow principle: repositioning should be verified with objective interface pressure measurement. They direct caregivers to check sacral pressure with an interface pressure meter, moving practice from routine turning to measured confirmation. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Continuous bedside pressure mapping functioned as a real-time “quality control” layer for staff by quickly exposing common setup and support-surface errors (eg, bottoming out, over-inflation, incorrect default settings) and guiding corrective actions at the bedside. Read Full Article
Title
Confirming Effective Off-Loading and Repositioning Using Continuous Bedside Pressure Mapping
Key Takeaway/s
Pressure mapping strengthened bedside workflow by allowing staff to visually confirm that a turn actually offloaded pressure, and by helping staff identify and remove hidden causes of high pressure (workflow-relevant problems that are easy to miss during routine care). Read Full Article
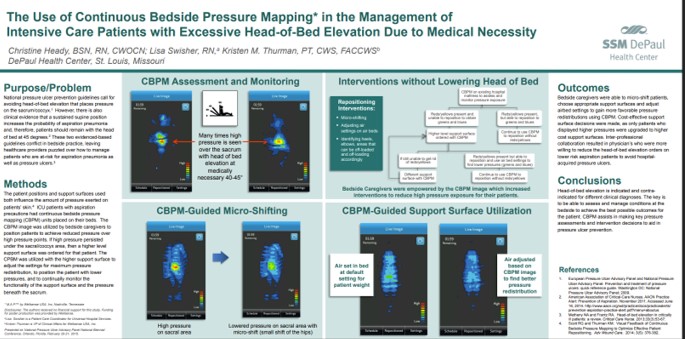
Title
Key Takeaway/s
When clinical requirements force elevated head-of-bed, pressure mapping supports safer, repeatable micro-adjustment workflows by showing staff when sacral pressures become excessive and guiding small positioning changes that meaningfully reduce pressure without disrupting the care plan. Read Full Article
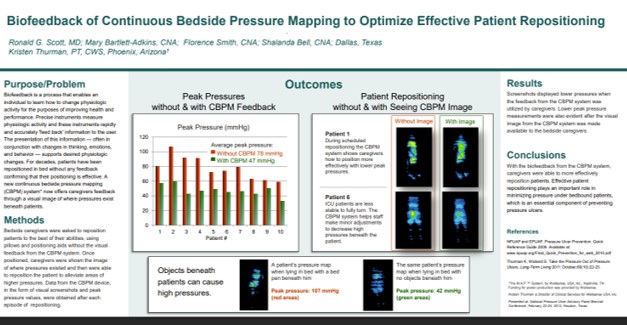
Title
Biofeedback of Continuous Bedside Pressure Mapping to Optimize Effective Patient Repositioning
Key Takeaway/s
This work highlights the training and technique benefit of biofeedback: staff can use live pressure visualization to refine repositioning in real time and standardize “what good looks like,” improving consistency of technique across caregivers. Read Full Article
Title
Visual Feedback of Continuous Bedside Pressure Mapping to Optimize Effective Patient Repositioning
Key Takeaway/s
Visual pressure feedback improves day-to-day nursing workflow by making repositioning more teachable and repeatable, helping caregivers quickly identify high-pressure areas and adjust positioning until pressure reduction is confirmed. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Real-time interface-pressure feedback supports better bedside practice by helping nurses identify effective repositioning targets, increasing pressure-reducing interventions, and reinforcing technique through immediate confirmation rather than assumption. Read Full Article
Title
Self-turning for Pressure Injury Prevention
Key Takeaway/s
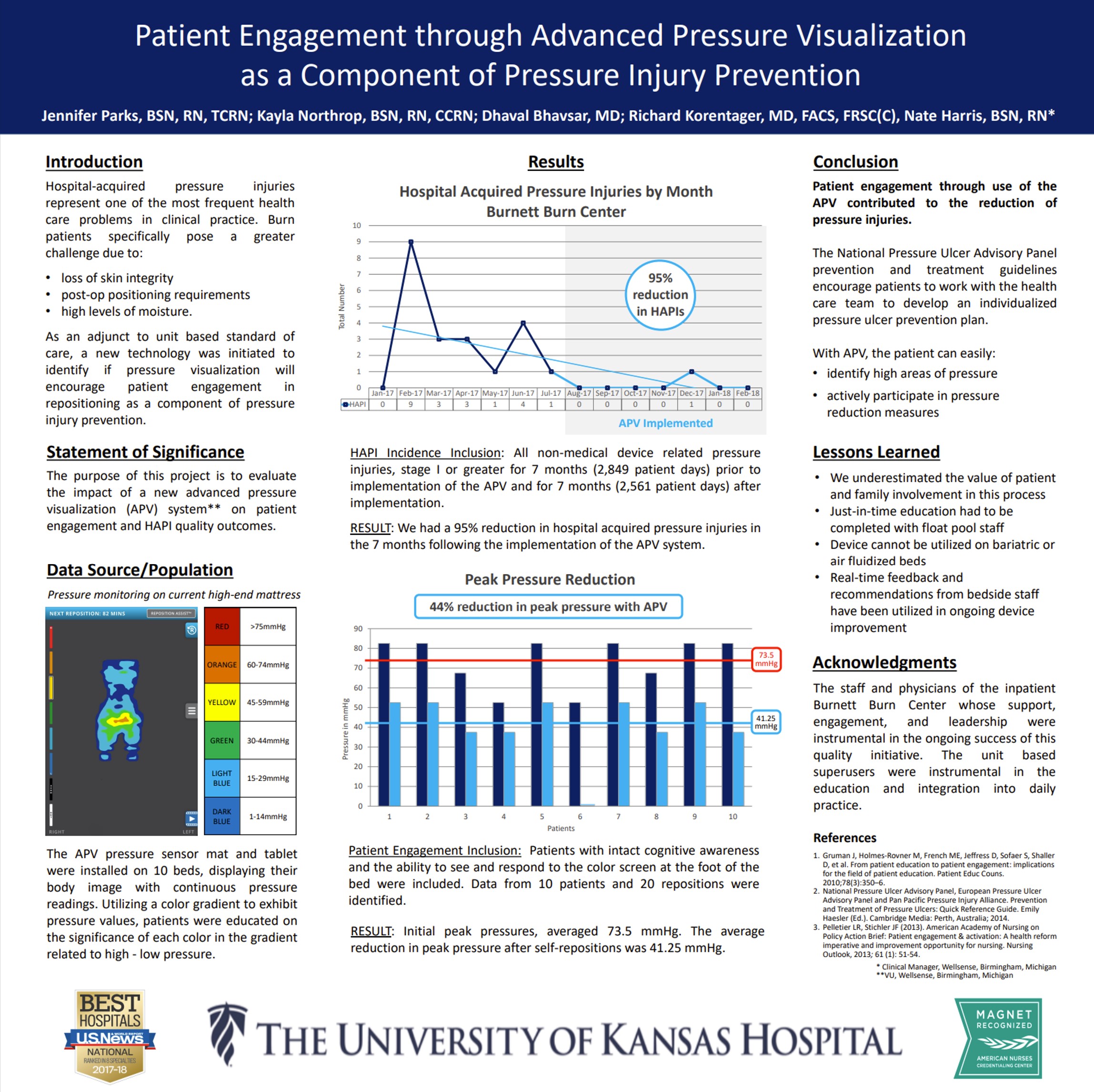
When appropriate patients were identified as able to self-turn, real-time pressure visualization helped them reposition themselves reliably with clear, immediate feedback. This demonstrates that pressure visualization can actively engage patients in their own pressure management, supporting safer self-directed turning when clinically appropriate. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
This study frames pressure visualization as a patient-facing tool: by making pressure visible, it motivates participation and supports behavior change around repositioning. The work reinforces that engagement improves when patients can see the cause-and-effect of their own movement on pressure. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In a veteran population, pressure visualization was used not only to guide clinical care but to empower patients and caregivers with understandable, visual information about pressure risk. This supports greater patient involvement in day-to-day positioning decisions and reinforces shared accountability for prevention and healing. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In two acute orthopedic trauma wards, patients and families reported the pressure visualization system was helpful, indicating strong engagement with the care process. The findings suggest that making pressure visible can improve patient and family understanding of repositioning goals and increase participation in prevention efforts. Read Full Article