Clinical Evidence – Select the category you want to view
Title
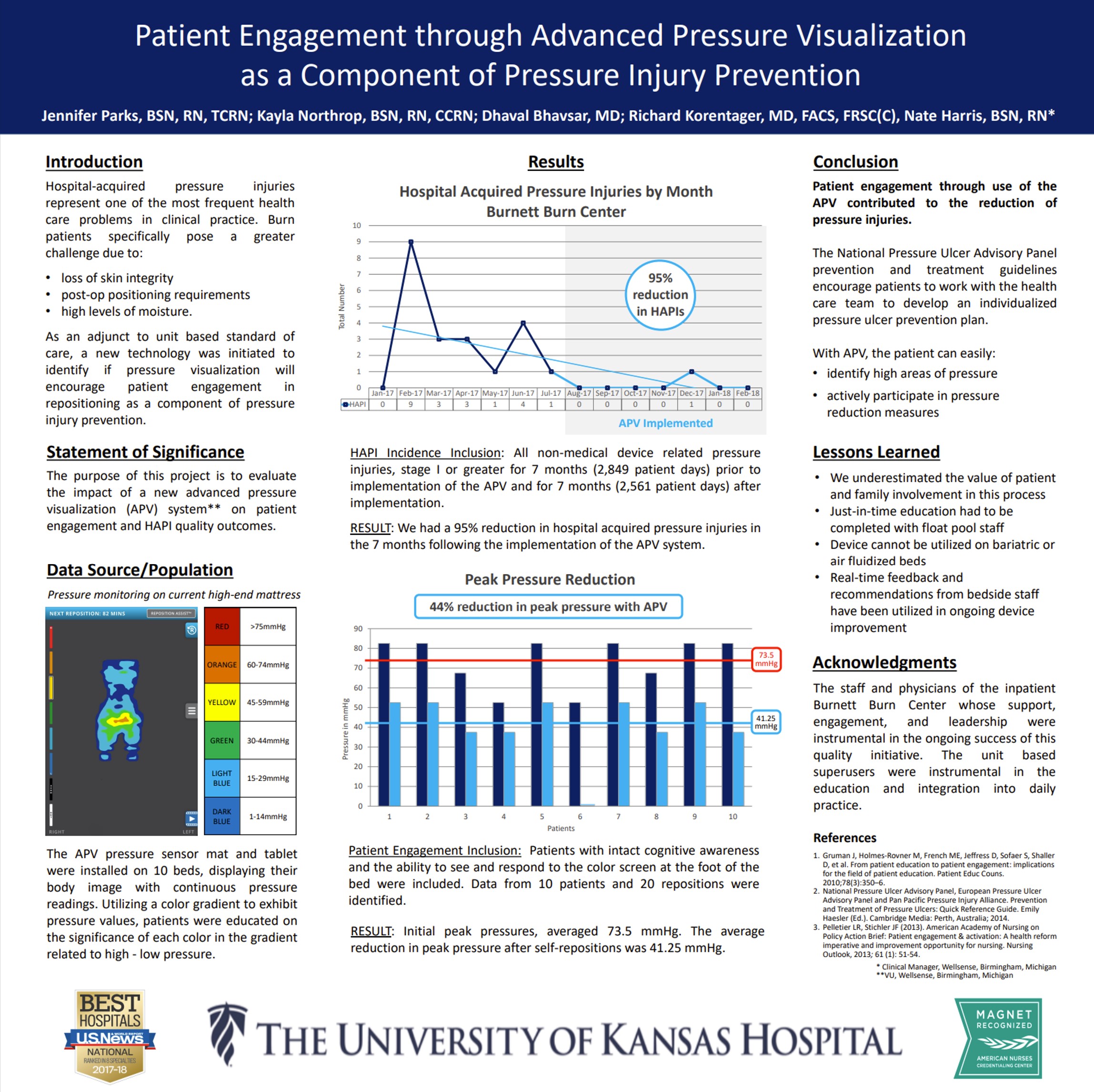
Visual Feedback of Continuous Bedside Pressure Mapping to Optimize Effective Patient Repositioning
Key Takeaway/s
Visual feedback from continuous bedside pressure mapping enabled caregivers to reposition patients more effectively, lowering high pressures and improving care. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Visual feedback from continuous bedside pressure mapping enabled caregivers to reposition patients more effectively, lowering high pressures and improving care Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
This UAB tertiary teaching-hospital study found that patients who developed hospital-acquired pressure ulcers incurred substantially higher costs and longer stays. Adjusted analyses showed costs of $29,048 vs $13,819 and length of stay of 20.9 vs 12.7 days, confirming pressure ulcers independently drive excess inpatient utilization beyond baseline severity. Read Full Article
Title
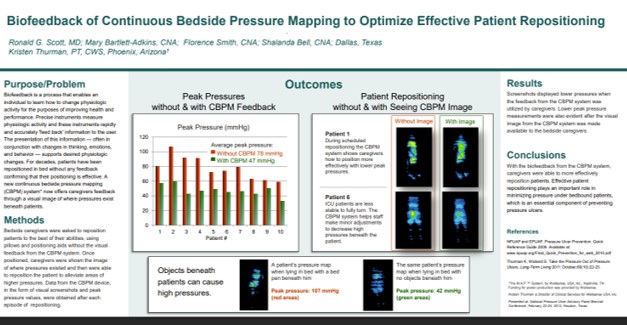
Biofeedback of Continuous Bedside Pressure Mapping to Optimize Effective Patient Repositioning
Key Takeaway/s
This clinical poster from Vanderbilt University Medical Center showed that real-time pressure visualization reduced median sacral pressure by 63%, with post-intervention pressure at 47 mmHg, a level consistent with very low interface pressure Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
This peer-reviewed study found that when staff repositioned residents using feedback from a real-time pressure mapping system, peak interface pressures were significantly reduced (P = .016) and more preventive interventions were implemented (P = .012), demonstrating that pressure visualization directly improves the effectiveness of repositioning Read Full Article
Title
Reducing Pressure Ulcer Development in the ICU
Key Takeaway/s
At Henry Ford Health System’s Medical ICU (Detroit), implementing real-time pressure visualization on 20 ICU beds was associated with a ~94% reduction in institution-related pressure ulcers versus the same months the prior year (16 to 1; 5% to 0.3%). The study reported no technical or safety issues and strong caregiver acceptance. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Real-time pressure mapping in ICUs, geriatric wards, operating rooms, and long-term care consistently showed that visual feedback allowed staff to identify high-risk zones, reposition more effectively, and prevent hospital-acquired pressure ulcers while also supporting wound healing. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
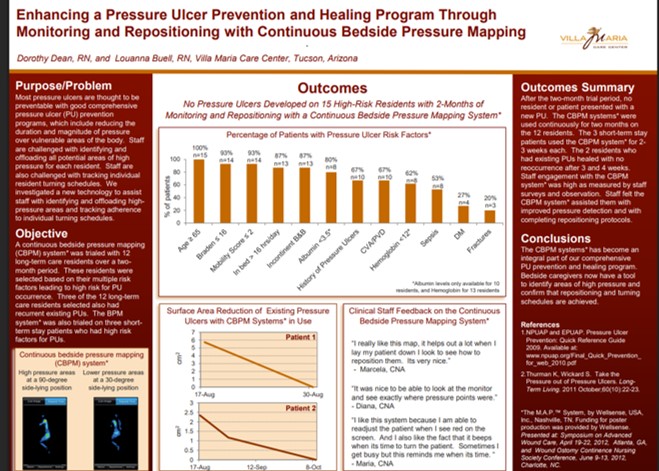
At Villa Maria Care Center, Continuous Bedside Pressure Mapping over two months prevented all new pressure ulcers in 15 high-risk residents, supported healing of existing ulcers with no recurrence, and became an integral part of the pressure ulcer prevention program. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
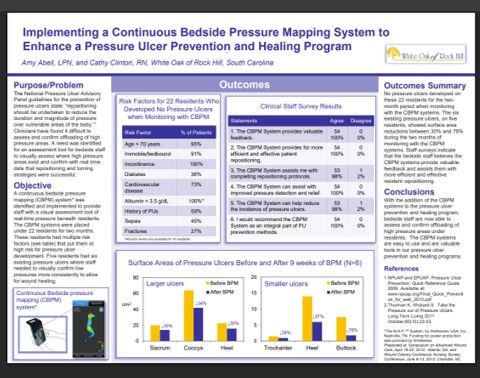
At White Oak of Rock Hill, no new pressure ulcers developed in 22 high-risk residents monitored with bedside pressure visualization, while existing ulcers showed 30–76% surface area reduction within 9 weeks Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
This Hopkins burn ICU study found that implementing real-time pressure mapping reduced HAPI-related care costs from about $6,750 to $3,800 per patient. These savings reflect direct pressure-injury treatment costs only (e.g., wound care), not systemic complications or extended hospitalization, and were driven by fewer and less severe pressure injuries Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
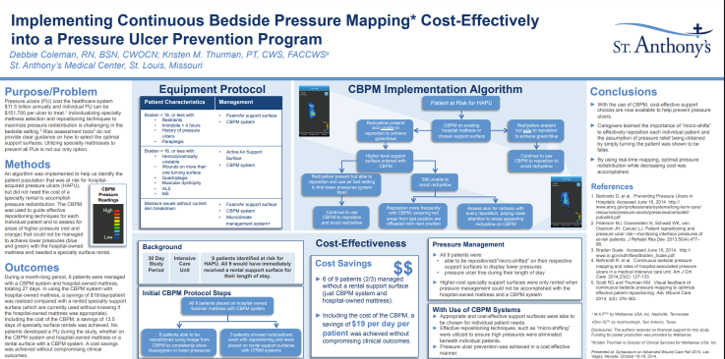
At St. Anthony’s Medical Center, Continuous Bedside Pressure Mapping enabled use of lower-cost support surfaces, reducing reliance on specialty rentals and delivering net savings of $19 per patient per day after including the cost of the visualization system itself. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In elderly care, pressure mapping directly supported staff education by improving pressure-injury awareness, strengthening repositioning decisions with visual feedback, and increasing the frequency and appropriateness of preventative interventions during routine care. Read Full Article
Title
Pressure Map Technology for Pressure Ulcer Patients: Can We Handle the Truth?
Key Takeaway/s
Pressure mapping improved workflow performance in a long-term acute care setting by reducing delays to scheduled turning, supporting more reliable execution of turning protocols, and creating clearer accountability around when repositioning actually occurs. Read Full Article
Title
Self-turning for Pressure Injury Prevention
Key Takeaway/s
Pressure visualization can be used as a structured education tool for appropriate patients, enabling them to learn and reliably perform self-repositioning with clear visual guidance, reducing staff burden while keeping turning technique verifiable. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Across multiple care settings, the evidence supports pressure visualization as a workforce enablement tool: it makes prevention practices more consistent, improves staff decision-making with real-time feedback, and strengthens training and standardization of repositioning technique. Read Full Article
Title
Self-turning for Pressure Injury Prevention
Key Takeaway/s
When appropriate patients were identified as able to self-turn, real-time pressure visualization helped them reposition themselves reliably with clear, immediate feedback. This demonstrates that pressure visualization can actively engage patients in their own pressure management, supporting safer self-directed turning when clinically appropriate. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
This study frames pressure visualization as a patient-facing tool: by making pressure visible, it motivates participation and supports behavior change around repositioning. The work reinforces that engagement improves when patients can see the cause-and-effect of their own movement on pressure. Read Full Article
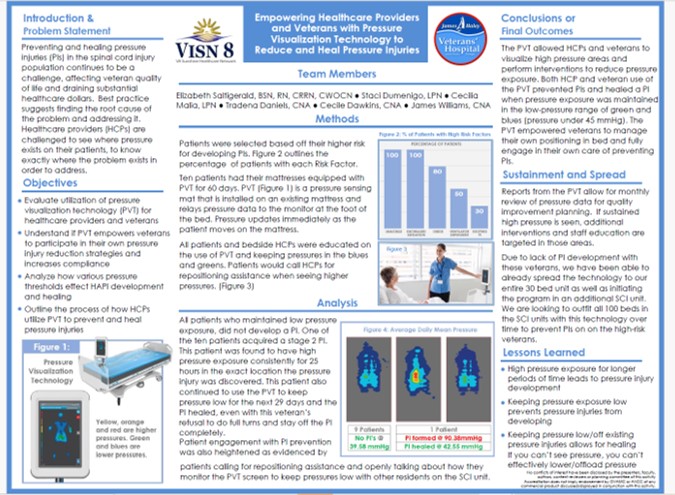
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In a veteran population, pressure visualization was used not only to guide clinical care but to empower patients and caregivers with understandable, visual information about pressure risk. This supports greater patient involvement in day-to-day positioning decisions and reinforces shared accountability for prevention and healing. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In two acute orthopedic trauma wards, patients and families reported the pressure visualization system was helpful, indicating strong engagement with the care process. The findings suggest that making pressure visible can improve patient and family understanding of repositioning goals and increase participation in prevention efforts. Read Full Article