Clinical Evidence – Select the category you want to view
Title
Efficacy of Monitoring Devices in Support of Prevention of Pressure Injuries
Key Takeaway/s
This Johns Hopkins-led meta-analysis reports that the use of pressure monitoring is associated with an 88% reduction in the risk of developing pressure injuries, demonstrating their effectiveness as a clinical prevention tool. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
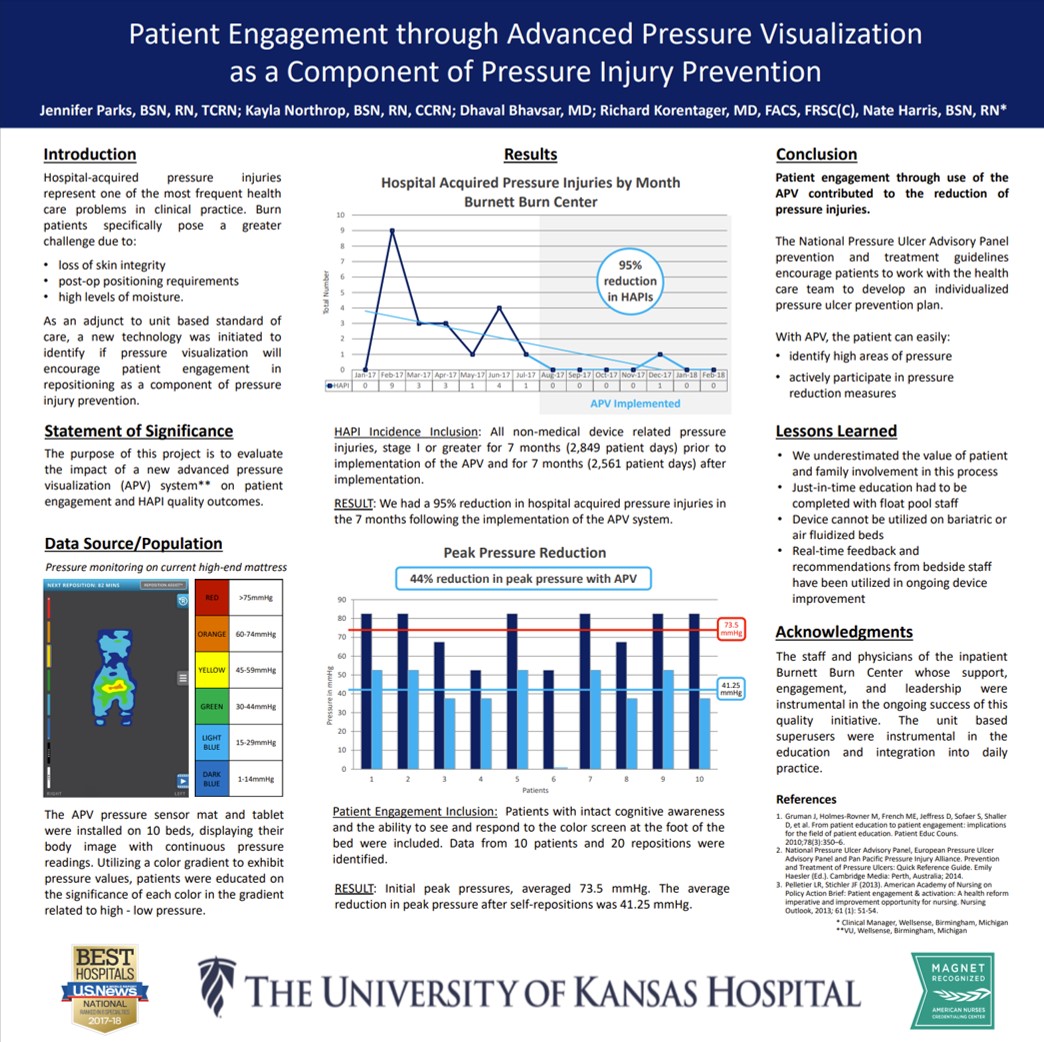
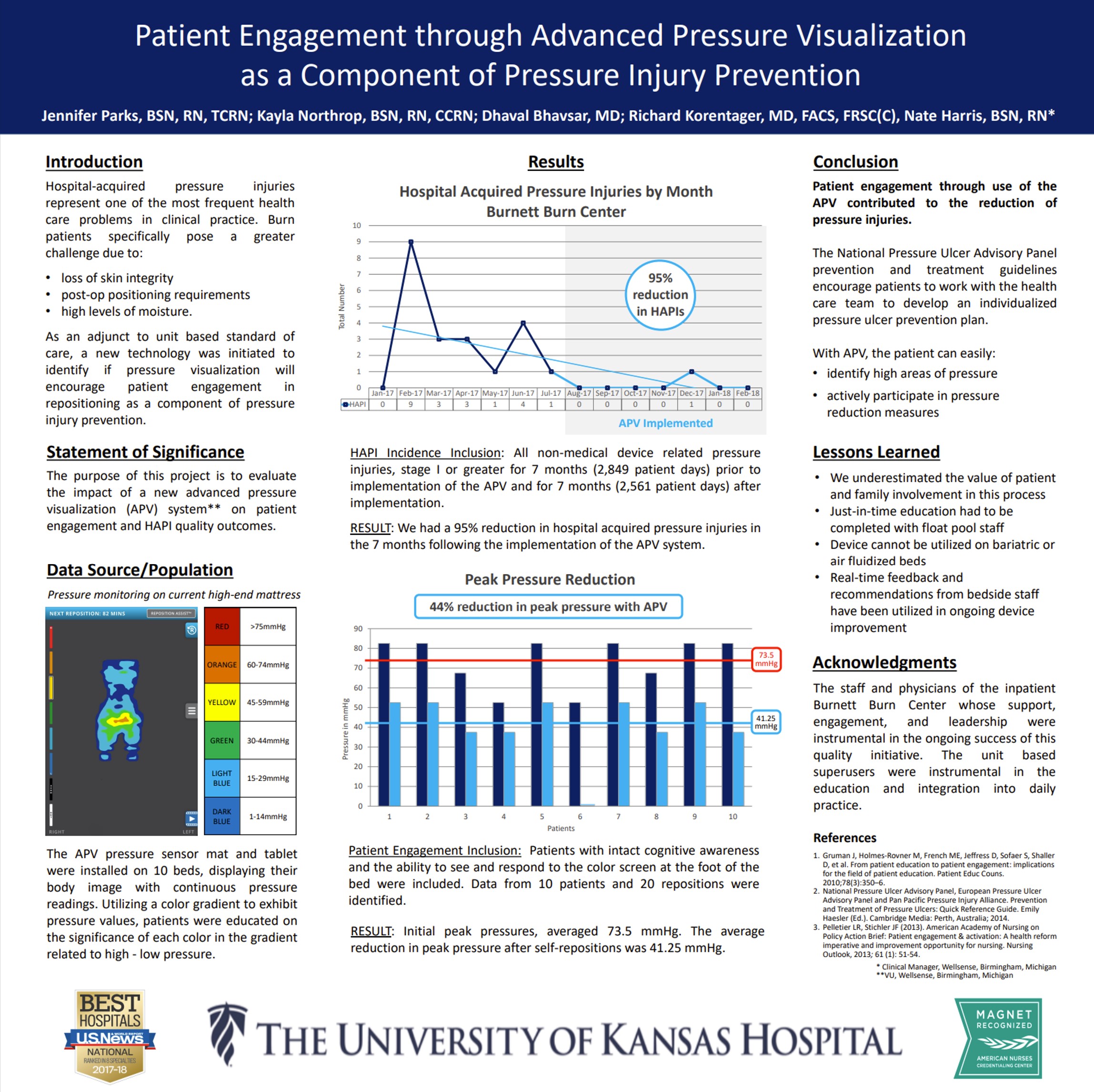
At the University of Kansas Hospital Burnett Burn Center, Advanced Pressure Visualization resulted in a 95% reduction in hospital-acquired pressure injuries (27 down to 1) and a 44% reduction in peak pressures, showing the effectiveness of patient engagement with real-time pressure feedback. Read Full Article
Title
Patient repositioning and pressure ulcer risk – Monitoring interface pressures of at-risk patients
Key Takeaway/s
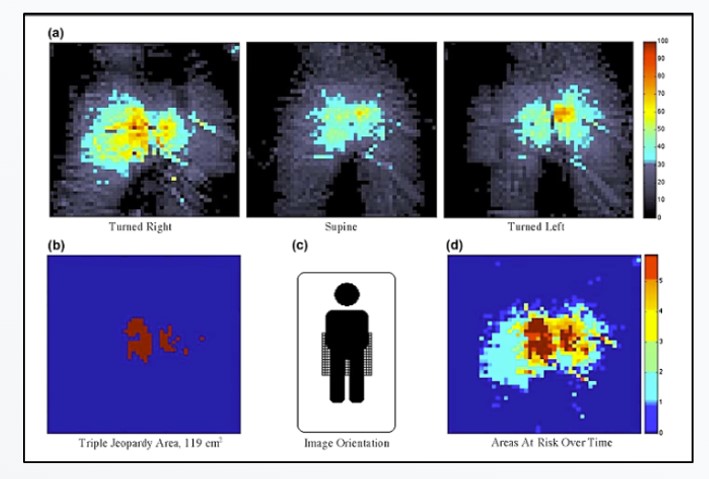
This peer-reviewed University of Florida study found that after repositioning, elevated sacral pressure persisted in over 95% of turns, leaving patients at ongoing pressure injury risk. The findings show that turning alone does not reliably offload pressure and that pressure visualization is needed to confirm effective offloading. Read Full Article
Title
Dynamic Physiologic Skin Monitoring to Enhance a Pressure Ulcer Prevention Program
Key Takeaway/s
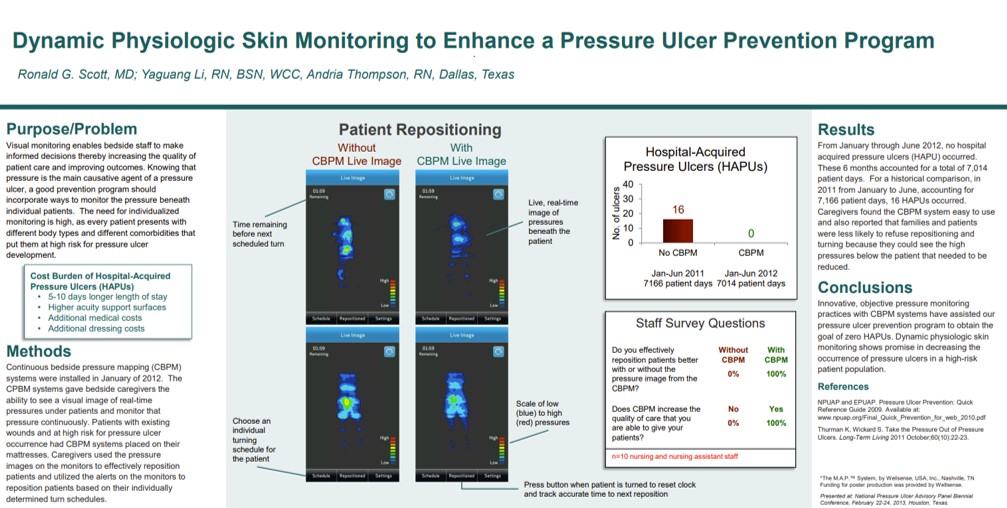
Methodist Dallas Medical Center achieved 100% elimination of hospital-acquired pressure ulcers over 7,014 patient days with continuous pressure visualization, compared to 16 HAPUs the prior year with visualization. Staff reported 100% agreement that visualization improved repositioning effectiveness and reduced pressure exposure. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In a retrospective analysis at Henry Ford Hospital’s medical ICU, continuous bedside pressure mapping reduced pressure ulcer incidence by 94% and was reported by staff to improve repositioning effectiveness, comfort, and adherence to protocols. Read Full Article
Title
Real-Time Pressure Assessment and Monitoring Improves Patient Care
Key Takeaway/s
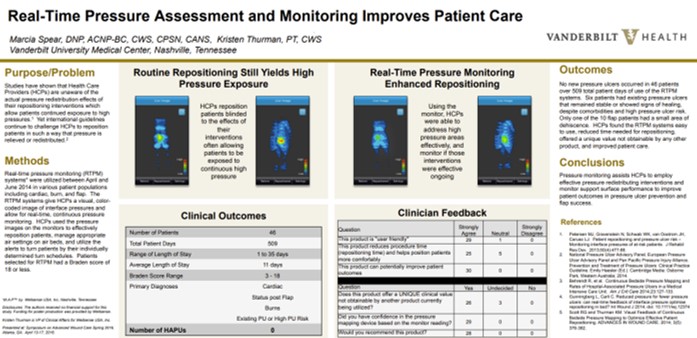
At Vanderbilt University Medical Center, real-time pressure visualization was used in 46 patients across 509 patient-days, resulting in zero new pressure injuries, high clinician satisfaction, improved repositioning effectiveness and patient comfort. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
At the Johns Hopkins Burn Center, real-time pressure mapping reduced the hospital-acquired pressure injury rate by 44.4%, eliminated full-thickness pressure injuries, and lowered costs by 43.8%, demonstrating significant effectiveness in the burn ICU. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
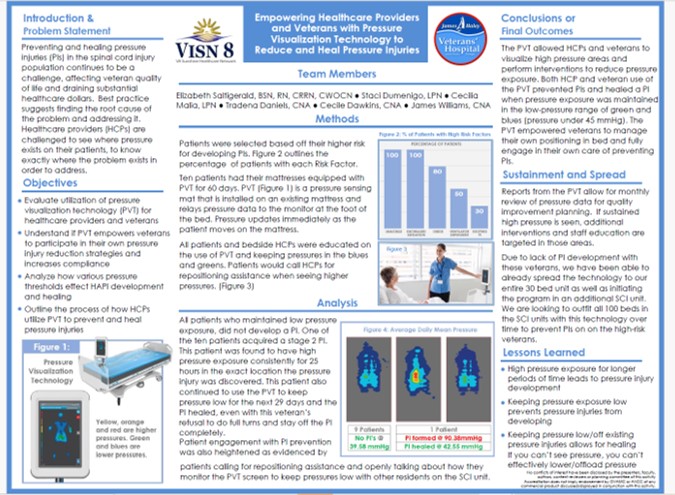
A clinical poster from the James A. Haley Veterans’ Hospital (VISN 8) showed that with pressure visualization technology, 90% of high-risk spinal cord injury patients avoided new pressure injuries, and existing Stage 2 injuries healed when pressure was reduced. Read Full Article
Title
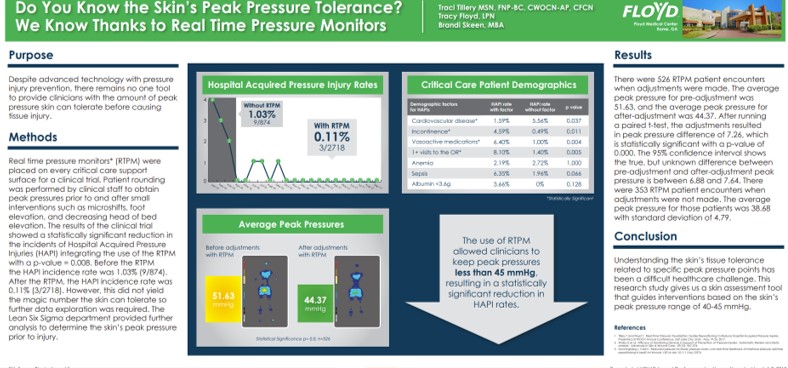
Do You Know the Skin’s Peak Pressure Tolerance? We Know Thanks to Real Time Pressure Monitors
Key Takeaway/s
This Floyd Medical Center poster showed that using real-time pressure monitoring reduced hospital-acquired pressure injuries (HAPIs) by nearly 90% and enabled staff to maintain peak pressures below ~45 mmHg, a threshold associated with significantly lower HAPI rates. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
This Hopkins burn ICU study found that implementing real-time pressure mapping reduced HAPI-related care costs from about $6,750 to $3,800 per patient. These savings reflect direct pressure-injury treatment costs only (e.g., wound care), not systemic complications or extended hospitalization, and were driven by fewer and less severe pressure injuries Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
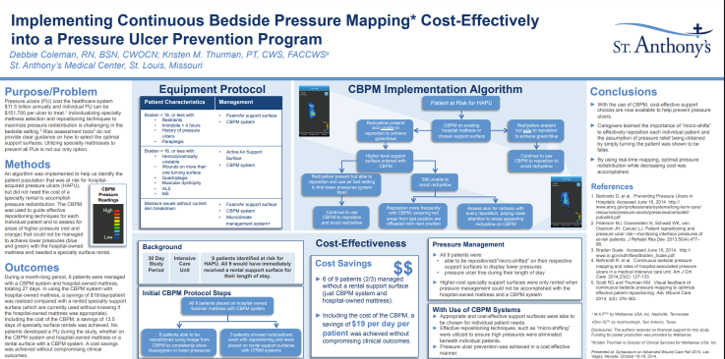
At St. Anthony’s Medical Center, Continuous Bedside Pressure Mapping enabled use of lower-cost support surfaces, reducing reliance on specialty rentals and delivering net savings of $19 per patient per day after including the cost of the visualization system itself. Read Full Article
Title
Pressure Mapping: A New Path to Pressure-Ulcer Prevention
Key Takeaway/s
Pressure mapping gives clinicians immediate visual feedback on where pressure remains, turning “best-practice” repositioning into a teachable, repeatable workflow. It helps staff validate that a turn or support-surface change actually relieved pressure, rather than relying on skin checks, habit, or patient report. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Real-time pressure feedback accelerates skills training by showing student nurses, instantly, whether a positioning change actually reduces interface pressure. This turns pressure-injury prevention from a theoretical lesson into a measurable competency and supports more consistent technique across learners and instructors. Read Full Article
Title
The wound/burn guidelines – 2: Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment for pressure ulcers
Key Takeaway/s
These guidelines reinforce a workflow principle: repositioning should be verified with objective interface pressure measurement. They direct caregivers to check sacral pressure with an interface pressure meter, moving practice from routine turning to measured confirmation. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Continuous bedside pressure mapping functioned as a real-time “quality control” layer for staff by quickly exposing common setup and support-surface errors (eg, bottoming out, over-inflation, incorrect default settings) and guiding corrective actions at the bedside. Read Full Article
Title
Confirming Effective Off-Loading and Repositioning Using Continuous Bedside Pressure Mapping
Key Takeaway/s
Pressure mapping strengthened bedside workflow by allowing staff to visually confirm that a turn actually offloaded pressure, and by helping staff identify and remove hidden causes of high pressure (workflow-relevant problems that are easy to miss during routine care). Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
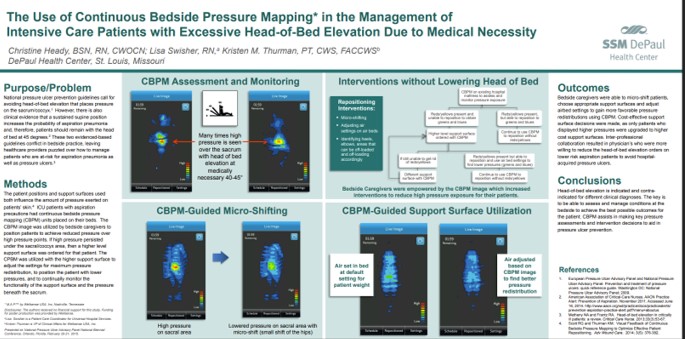
When clinical requirements force elevated head-of-bed, pressure mapping supports safer, repeatable micro-adjustment workflows by showing staff when sacral pressures become excessive and guiding small positioning changes that meaningfully reduce pressure without disrupting the care plan. Read Full Article
Title
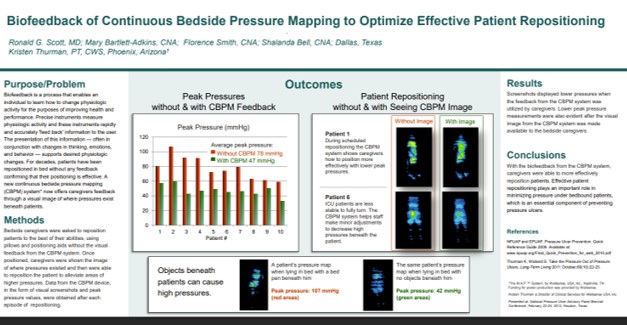
Biofeedback of Continuous Bedside Pressure Mapping to Optimize Effective Patient Repositioning
Key Takeaway/s
This work highlights the training and technique benefit of biofeedback: staff can use live pressure visualization to refine repositioning in real time and standardize “what good looks like,” improving consistency of technique across caregivers. Read Full Article
Title
Visual Feedback of Continuous Bedside Pressure Mapping to Optimize Effective Patient Repositioning
Key Takeaway/s
Visual pressure feedback improves day-to-day nursing workflow by making repositioning more teachable and repeatable, helping caregivers quickly identify high-pressure areas and adjust positioning until pressure reduction is confirmed. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
Real-time interface-pressure feedback supports better bedside practice by helping nurses identify effective repositioning targets, increasing pressure-reducing interventions, and reinforcing technique through immediate confirmation rather than assumption. Read Full Article
Title
Self-turning for Pressure Injury Prevention
Key Takeaway/s
When appropriate patients were identified as able to self-turn, real-time pressure visualization helped them reposition themselves reliably with clear, immediate feedback. This demonstrates that pressure visualization can actively engage patients in their own pressure management, supporting safer self-directed turning when clinically appropriate. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
This study frames pressure visualization as a patient-facing tool: by making pressure visible, it motivates participation and supports behavior change around repositioning. The work reinforces that engagement improves when patients can see the cause-and-effect of their own movement on pressure. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In a veteran population, pressure visualization was used not only to guide clinical care but to empower patients and caregivers with understandable, visual information about pressure risk. This supports greater patient involvement in day-to-day positioning decisions and reinforces shared accountability for prevention and healing. Read Full Article
Title
Key Takeaway/s
In two acute orthopedic trauma wards, patients and families reported the pressure visualization system was helpful, indicating strong engagement with the care process. The findings suggest that making pressure visible can improve patient and family understanding of repositioning goals and increase participation in prevention efforts. Read Full Article